Type of depositional Environments
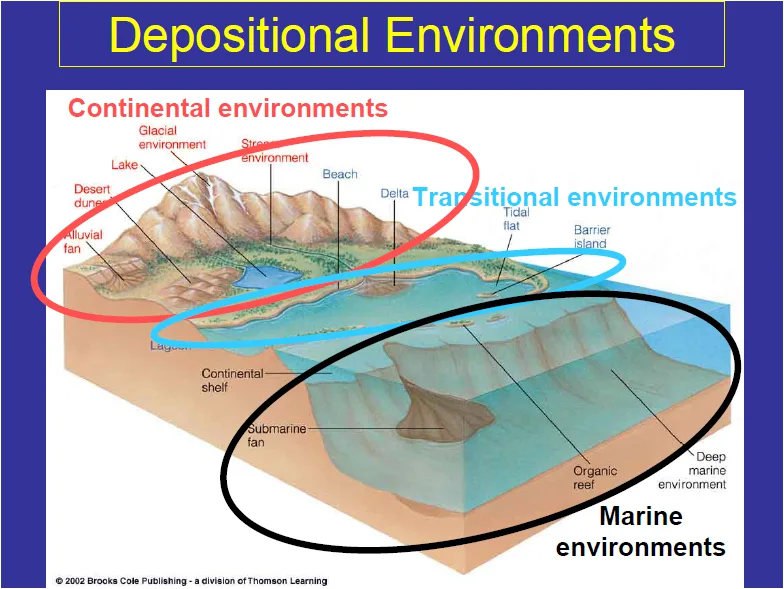
- CONTINENTAL
- Alluvial – type of Fluvial deposite. Caused by moving water in a fan shape (Alluvial Fan) and containing mostly impermeable and nonporous sediments well sorted.
- Aeolian – Processes due to wind activity. Often in deserts and coastal regions and well sorted, large scale cross-beds
- Fluvial -processes due to moving water, mainly streams. Common sediments are gravel, sand, and silt.
- Lacustrine– processes due to moving water, mainly lakes. Common sediments are sand, silt, and clay.
- TRANSITIONAL
- Deltaic – Silt deposition landform at the mouth of a river (possible cross beds, ripple marks)[5] Common sediments are sand, silt, and clay.
- Tidal– processes due to tidal currents, creates tidal flats (fine-grained, ripple marks, cross-beds). Common sediments are silt and clay
- Lagoonal– A shallow body of water separated from a larger body of water by barrier islands or reefs. Little transportation, creates lagoon bottom environment. Common sediments are carbonates (in tropical climates).
- Beach– Area of loose particles at the edge of the sea or other body of water. Caused by waves and longshore currents. Creates beaches, spits, and sandbars with the common sediments of gravel and sand.
- Lake– A body of relatively still water, in a basin surrounded by land
- MARINE
- Shallow water marine environment – processes due to waves and tidal currents, creates shelves and slopes, lagoons. Common sediments are carbonates (in tropical climates) or sand, silt, and clay (elsewhere)
- Upper-shoreface– The portion of the seafloor that is shallow enough to be agitated by everyday wave action
- Lower-shoreface– The portion of the seafloor, and the sedimentary depositional environment, that lies below the everyday wave base
- Deep water marine environment – Flat area on the deep ocean floor (abyssal plains) caused by ocean currents. Common sediments are clay, carbonate mud, silica mud.
- Reef– A bar of rock, sand, coral or similar material, lying beneath the surface of water caused by waves and tidal currents. Also creates adjacent basins. Common sediments are carbonates.
- OTHERS
- Evaporite – A water-soluble mineral sediment formed by evaporation from an aqueous solution
- Glacial
- Till- angular to rounded grains, poorly sorted, unstratified (massive)
- Outwash– ripple marks, cross-beds, similar to stream channel
- Volcanic
- Tsunami – Sedimentary unit deposited by a tsunami

Responses